Kublr, as a leading Kubernetes cluster management platform, offers organizations the ability to deploy and manage Kubernetes clusters seamlessly across multiple cloud providers. Its user-friendly interface, comprehensive feature set, and strong focus on security make it an indispensable tool for modern enterprises.
A standout feature of Kublr is its integration with Keycloak, enabling advanced centralized identity management, authentication and access control functionality out of the box. This capability empowers teams to efficiently manage RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) across Kubernetes clusters with ease. For enterprises using Microsoft Active Directory (AD), Kublr simplifies authentication and authorization processes, offering seamless integration that aligns with existing organizational security policies.
This article explores how Kublr integrates with Active Directory and leverages Keycloak to deliver secure, scalable, and easy-to-manage Kubernetes environments.
Prerequisites:
The following Active Directory (AD) groups should be created to manage access within Kublr efficiently:
Also need to create an Active Directory (AD) account with read-only permissions to facilitate secure access to AD from Keycloak.
In Kublr Control Plane:
Login to Keycloak with admin account.
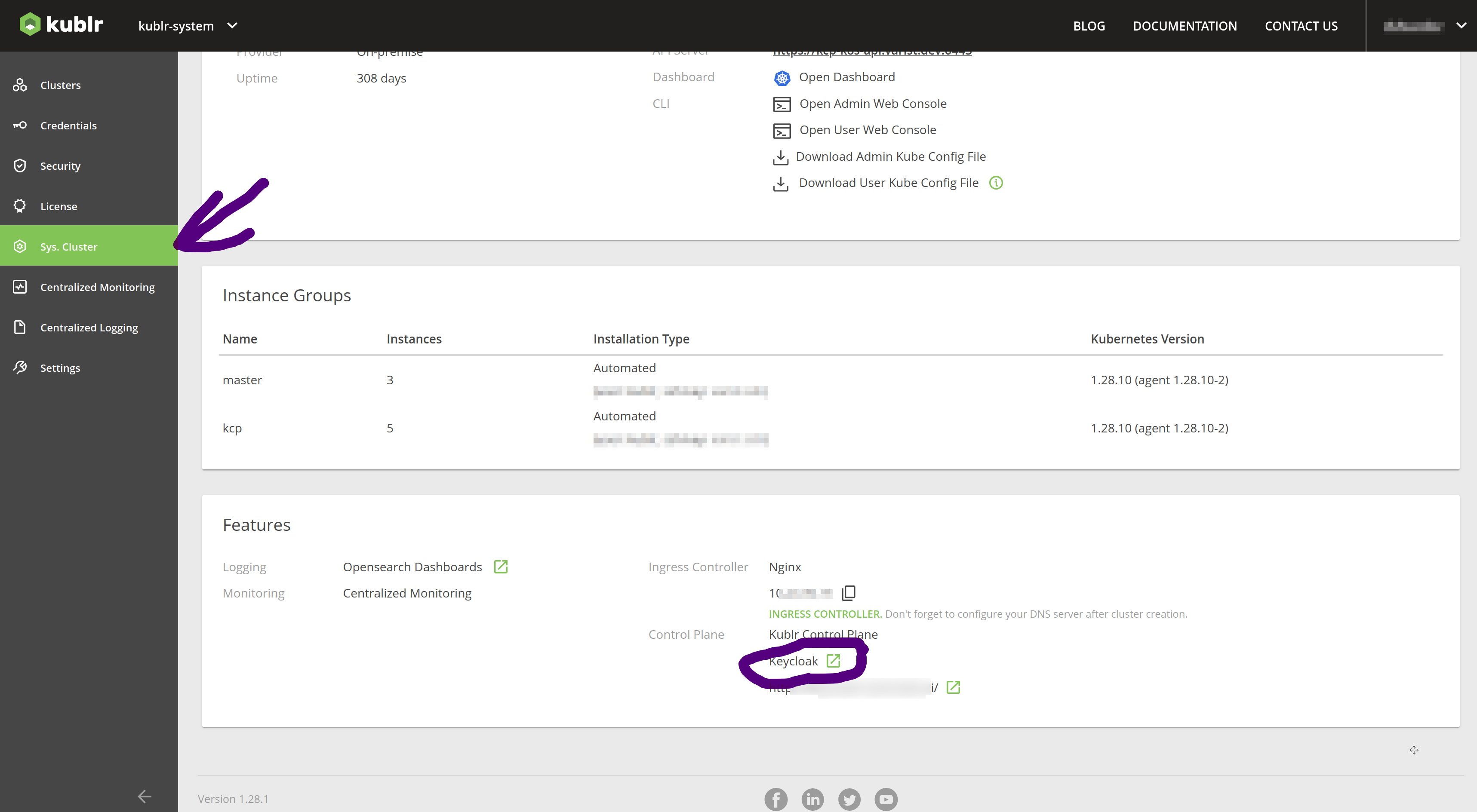
In Keycloak:
Make sure you have selected kublr-ui realm.
In User Federation section, please select Add new provider and choose LDAP
Configure the connection settings:
For Synchronization settings, enable the following:
Save all changes, and then navigate to tab Mappers inside created User Federation provider.
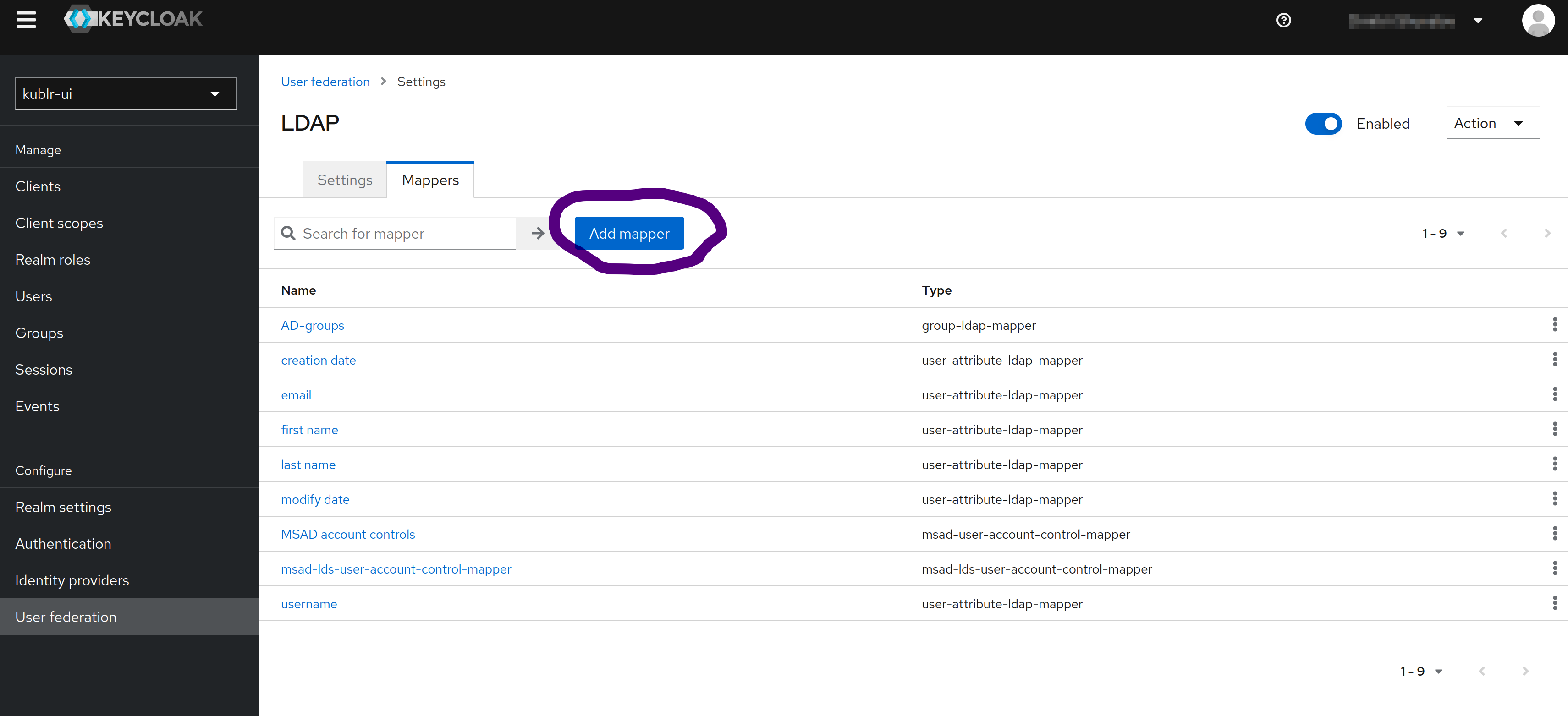
Using Add mapper button, add the following mapper:
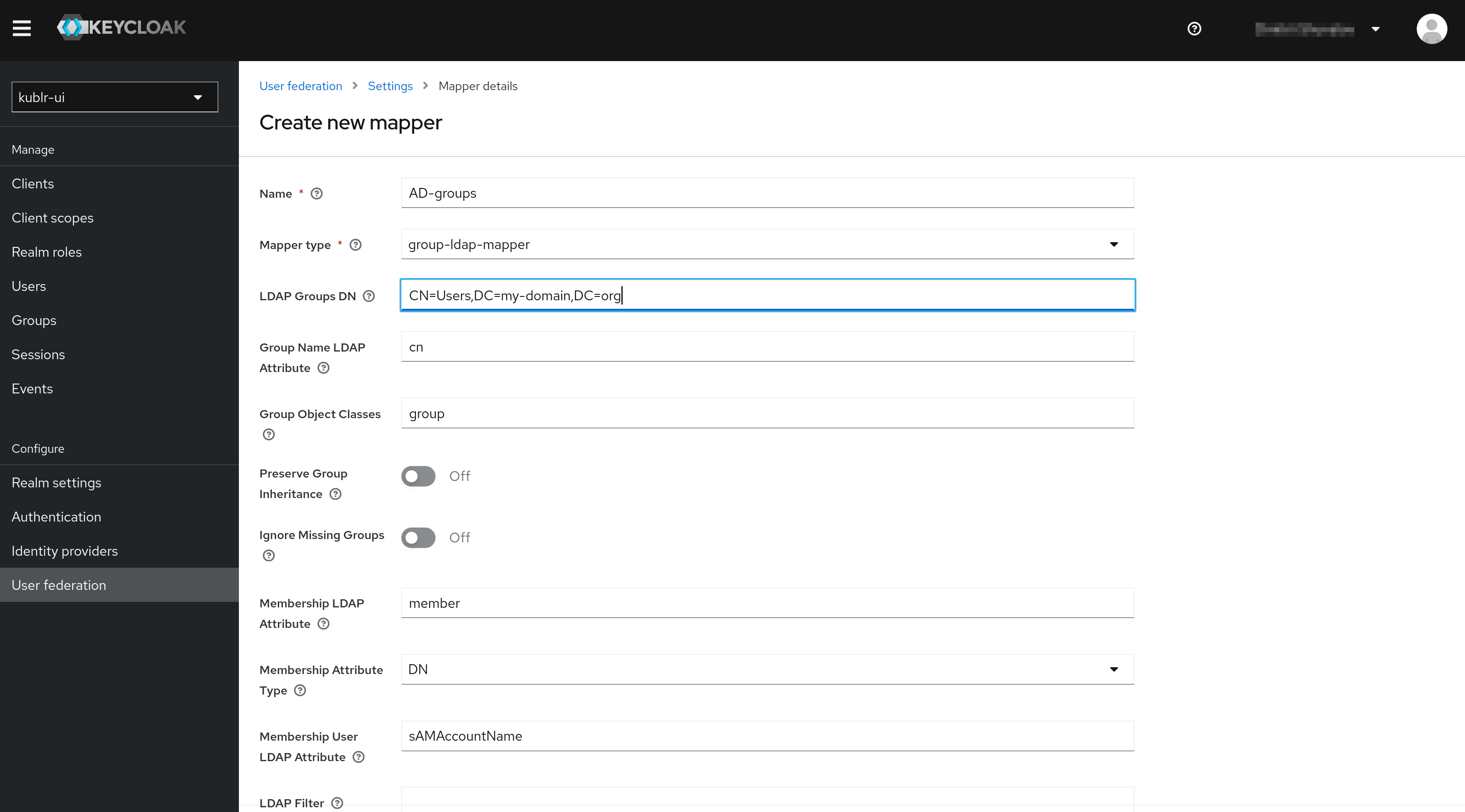
Please refer to Kublr RBAC documentation on how to configure Kublr RBAC.
In order to get the RBAC model implemented, we have the following Kublr Security roles and bindings configured:
| Default aligned | Center aligned | Center aligned | Center aligned | Center aligned |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AllSpacesViewer | GlobalRole | Space: list | AllSpacesViewer | KublrClusterAdmins KublrDevelopers KublrProdOperations KublrViewers |
| KublrClusterAdmins | GlobalRole | Space: list, get Cluster, Cluster/id: list, get, put cluster/applications, cluster/proxy, cluster/metrics: * Secret: list | KublrClusterAdmins-prod KublrClusterAdmins-dev | prod dev |
| KublrDevelopers | GlobalRole | Space, cluster, cluster/config, cluster/proxy, cluster/dashboard, cluster/terminal, cluster/id, cluster/metrics: list, get | KublrDevelopers | dev |
| KublrProdOperations | GlobalRole | Space, cluster, cluster/config, cluster/proxy, cluster/dashboard, cluster/terminal, cluster/id, cluster/metrics: list, get | KublrProdOperations | prod |
| KublrViewers | GlobalRole | Space, cluster, cluster/config, cluster/proxy, cluster/dashboard, cluster/terminal, cluster/id, cluster/metrics: list, get | KublrViewers-prod KublrViewers-dev | prod dev |
The following roles and role bindings have been configured in the existing clusters:
| Environment | Role | Description | Role Binding | Namespace | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control plane | N/A | No specific configuration, as this Kubernetes cluster should be accessed only by KublrFullAdmins members | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| DEV | ClusterOverview | nodes: list | ClusterOverview | Global | To groups: KublrDevelopers KublrViewers Allows members of these groups to see cluster metrics and “instances” tab. Required for collecting nodes list and metrics (CPU, memory, storage). |
| admin | Predefined K8s role | KublrDevelopers-default | default | Admin role for default namespace for group KublrDevelopers. | |
| View | Predefined K8s role | KublrViewers-default | default | Viewer role for default namespace for group KublrViewers. | |
| admin | Predefined K8s role | KublrDevelopers-develop | develop | Admin role for develop namespace for group KublrDevelopers. | |
| View | Predefined K8s role | KublrViewers-develop | develop | Viewer role for develop namespace for group KublrViewers. | |
| PROD | ClusterOverview | nodes: list | ClusterOverview | Global | To groups: KublrProdOperations KublrViewers Allows members of these groups to see cluster metrics and “instances” tab. Required for collecting nodes list and metrics (CPU, memory, storage). |
| admin | Predefined K8s role | KublrProdOperations-default | default | Admin role for default namespace for group KublrProdOperations. | |
| View | Predefined K8s role | KublrViewers-default | default | Viewer role for default namespace for group KublrViewers. | |
| admin | Predefined K8s role | KublrProdOperations-prod | prod | Admin role for prod namespace for group KublrProdOperations. | |
| View | Predefined K8s role | KublrViewers-prod | prod | Viewer role for prod namespace for group KublrViewers. |
Kublr offers seamless integration with a variety of directory services, including Active Directory, FreeIPA, and OpenLDAP. This flexibility ensures that your organization can leverage existing authentication systems to manage user access and permissions efficiently.
Integrating Kublr with these services is a straightforward process, requiring minimal effort. The steps are consistent across different directory services, with only minor adjustments to attribute names based on the specific schema used by your directory. For instance, FreeIPA or OpenLDAP might use custom attribute mappings, but Kublr’s configuration flexibility ensures a smooth setup.
With this robust compatibility, Kublr not only simplifies the integration process but also enhances security by aligning with your enterprise’s centralized identity management. This allows teams to manage access seamlessly, enforce policies, and maintain compliance with organizational standards.
No matter which directory service you use, Kublr’s intuitive interface and comprehensive documentation make the integration process effortless. By supporting a wide range of directory services, Kublr ensures that your Kubernetes environment is fully equipped to meet the demands of modern enterprise operations.
Integrating Active Directory with Kubernetes can be a daunting task, but Kublr makes it simple, secure, and scalable. By leveraging Keycloak, organizations can streamline authentication, automate access control, and ensure compliance with corporate security policies. Whether you’re managing one cluster or dozens across multiple clouds, Kublr provides the tools you need to succeed.
To learn more about Kublr and its advanced features, visit Kublr’s website.