This document explains the main aspects of the Kublr Backup/Restore feature. Kublr Cluster Backup make snapshots of all cluster volumes, including:
Each set of volume snapshots is called backup snapshot. You can restore a cluster from specific backup snapshot.
Kublr does not make application-level backups or external-services backups (RDS or DynamoDB for example).
Kublr backups are created and purged according to the backup schedule. The schedule defines:
The Kublr Platform uses AWS API and cluster’s AWS credentials to create volume snapshots and/or to remove old snapshots.


For each Kublr backup you can get:
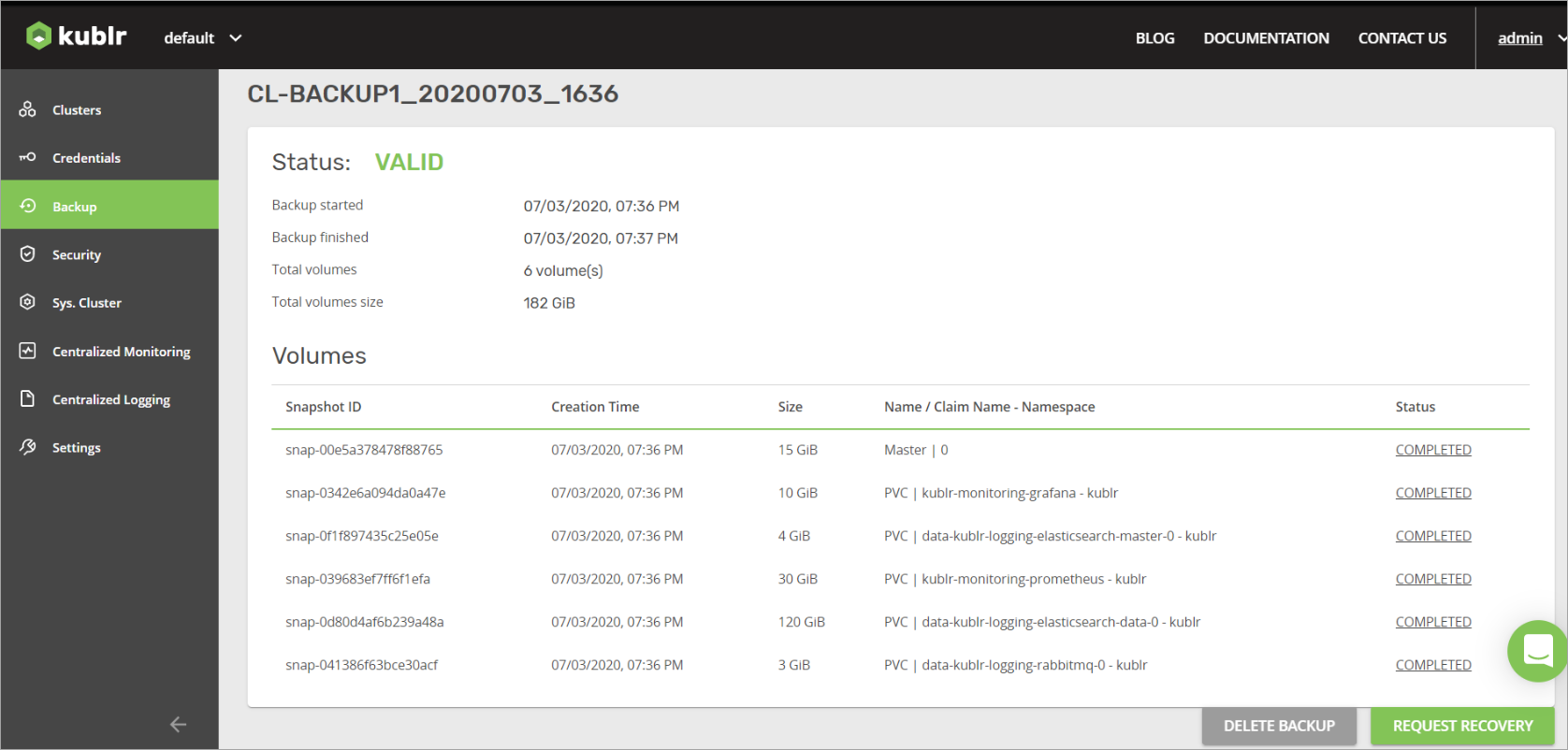
You can restore only deleted clusters. The cluster recovery process is similar to cluster creation.
To restore a deleted cluster:
In Kublr, on the left menu, click Backup.
Click the name of the deleted cluster. The page for managing cluster backups is displayed.
In the Backup List, to the right of the appropriate backup, click the Request Recovery button.
_backups-backup_list.png#left#nomargin)
Note Alternatively, you can enter the page of the backup and click the REQUEST RECOVERY button.
Confirm the cluster recovery.
Additionally, you can:
Does Kublr guarantee cluster backup consistency?
No, Kublr can’t guarantee this. Because cluster nodes are not stopped during the backup procedure, snapshots typically have different creation times.
Currently Kublr supports backup for AWS cloud providers only. Additional support for other cloud providers, as well as instructions for on-premises installations, will be available in future versions of Kublr.
At this moment Kublr cannot restore backups over existing clusters. Please remove the cluster before restoring it from the backup.
Please read the Kublr Release Notes about known issues related to backups.